How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and control mechanisms to advanced techniques in photography and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone navigation, ensuring you’re well-equipped to handle your drone with confidence and expertise.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. Understanding the fundamentals of flight mechanics, coupled with a comprehensive understanding of safety protocols and legal regulations, is crucial for responsible and successful drone piloting. This guide aims to bridge the gap between theory and practice, empowering you to confidently take to the skies.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation. It minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures optimal performance. This involves systematically checking various components before each flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection includes verifying battery levels, inspecting propellers for damage, and confirming GPS signal acquisition. Failing to perform these checks can lead to unexpected malfunctions mid-flight.
- Check battery voltage and remaining flight time. Ensure batteries are fully charged and properly connected.
- Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, bends, or other damage. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired before initiating takeoff. A weak signal can result in inaccurate positioning and flight instability.
- Inspect the drone’s body for any visible damage or loose parts.
- Verify all control surfaces (e.g., gimbal, camera) are functioning correctly.
Sample Pre-Flight Checklist
Using a checklist helps standardize the pre-flight process, reducing the likelihood of overlooking critical steps. The following table provides a sample checklist, adaptable to various drone models.
| Manufacturer | Model | Item | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI | Mavic 3 | Battery Level | ✓ |
| DJI | Mavic 3 | Propeller Condition | ✓ |
| DJI | Mavic 3 | GPS Signal | ✓ |
| Autel | Evo II Pro | Battery Level | ✓ |
| Autel | Evo II Pro | Propeller Condition | ✓ |
| Autel | Evo II Pro | GPS Signal | ✓ |
Safety Procedures
Safety protocols are paramount in drone operation. Emergency procedures and obstacle avoidance are key aspects of safe flying.
- Emergency Landing Protocols: In case of unexpected malfunctions, immediately initiate a controlled descent. Prioritize a safe landing area, away from people and obstacles.
- Obstacle Avoidance Techniques: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles, utilizing the drone’s obstacle avoidance sensors and visual observation. Plan your flight path carefully to avoid potential hazards.
- Awareness of Surroundings: Constantly monitor your surroundings for potential hazards such as power lines, trees, and other aircraft.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section details the basic controls and various flight modes.
Drone Controls
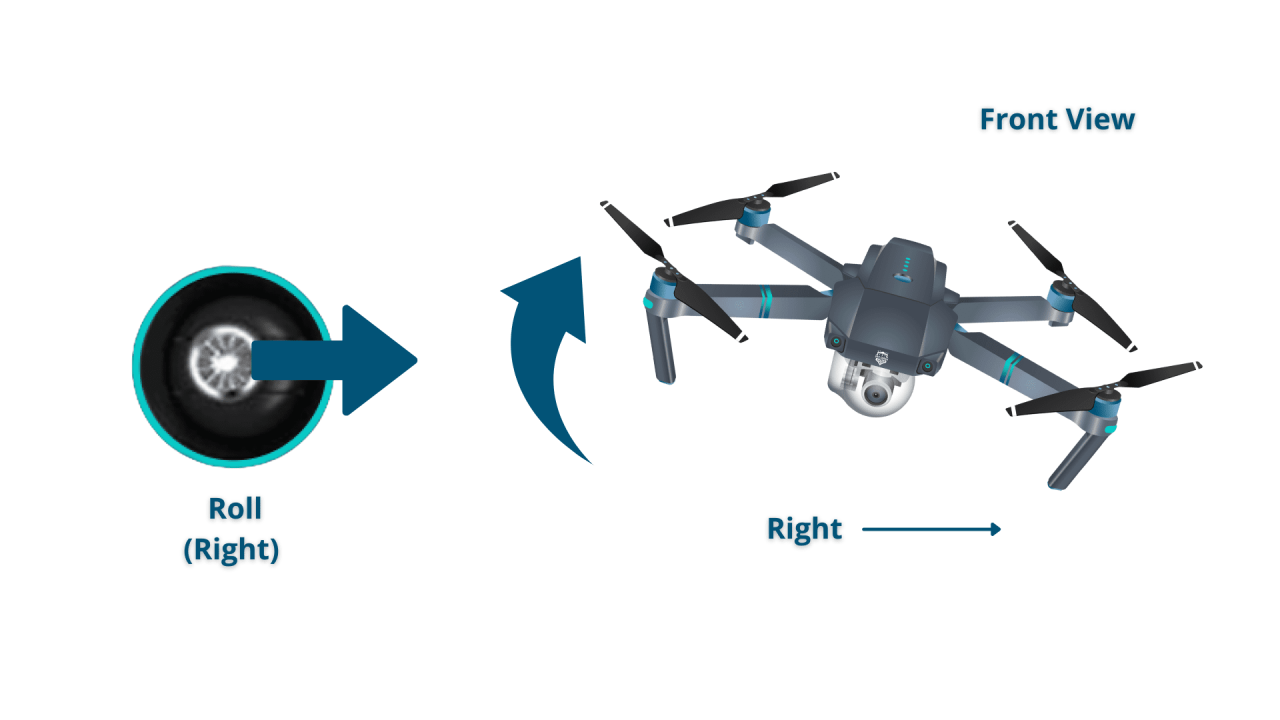
Most drones utilize four basic controls: throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. These controls manipulate the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right (sideways).
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding their functionalities is critical for adapting to different flight conditions.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude, simplifying horizontal movement.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS signals for precise positioning and stable flight, even in windy conditions.
- Attitude Mode: Offers more responsive control, ideal for precise maneuvers but requires more skill.
Control Interface Comparison
Control interfaces vary across drone models, impacting ease of use and functionality. Some offer intuitive touchscreens, while others utilize more traditional controllers.
- DJI drones often feature user-friendly apps with detailed flight information and settings.
- Autel drones may utilize more specialized controllers with customizable buttons and settings.
Navigating with GPS Coordinates

Precise navigation using GPS coordinates enhances the accuracy and efficiency of drone flights, particularly for mapping or surveying applications.
- Input the desired GPS coordinates into the drone’s flight controller or app.
- Engage the GPS mode on the drone.
- Initiate the flight, allowing the drone to autonomously navigate to the specified coordinates.
- Monitor the drone’s progress, making adjustments as needed.
- Upon reaching the destination, execute a safe landing procedure.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
Safe and efficient takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of your drone. This section Artikels the proper techniques.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A smooth and controlled takeoff minimizes the risk of collisions and ensures a stable flight. Begin by selecting a suitable, open area free from obstacles.
- Ensure the drone is calibrated and has a strong GPS signal.
- Slowly increase the throttle, allowing the drone to ascend vertically.
- Once airborne, gently maneuver the drone to your desired position.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Maintaining stable flight requires careful control and adaptation to varying conditions. Wind, for instance, can significantly impact drone stability.
- In windy conditions, reduce speed and maintain a lower altitude.
- Utilize the drone’s stabilization features to compensate for wind gusts.
- Practice smooth and controlled movements to avoid sudden changes in direction or altitude.
Safe Landing Procedure
A controlled landing is just as important as a safe takeoff. Choose a suitable landing area and execute the landing sequence carefully.
- Gradually decrease the throttle, ensuring a slow and controlled descent.
- Maintain a steady approach to the landing area.
- Once the drone is close to the ground, gently lower it to a complete stop.
Optimal Flight Path
The optimal flight path depends on the specific task, but a common pattern involves a sequence of ascending, traversing, and descending maneuvers.
Imagine a flight path resembling a wide, shallow “U”. The drone ascends to its operational altitude, traverses horizontally to capture footage, and then descends to the landing point. Each stage requires smooth transitions and consideration of wind conditions and potential obstacles.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section offers tips and techniques for enhancing your drone’s photographic capabilities.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving professional-looking aerial footage requires attention to detail in camera settings and composition.
- Camera Settings: Adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture based on lighting conditions to optimize image quality and minimize noise.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Lighting: The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) often provides the most visually appealing lighting conditions.
Camera Settings for Different Lighting

Different lighting conditions require adjustments to camera settings to maintain optimal image quality.
- Bright Sunlight: Lower ISO, faster shutter speed.
- Overcast Conditions: Higher ISO, slower shutter speed.
- Low Light: Higher ISO, slower shutter speed, potentially wider aperture.
Camera Angles and Compositions
Varying camera angles and compositions can significantly enhance the visual appeal of aerial footage.
- High-angle shots: Provide a broad overview of the scene.
- Low-angle shots: Emphasize the scale and grandeur of the subject.
- Side-angle shots: Offer a dynamic and engaging perspective.
Post-Processing Techniques
Post-processing enhances the quality and visual impact of drone footage.
- Color Grading: Adjust color balance and saturation to create a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing look.
- Stabilization: Smooth out shaky footage using software like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve.
- Sharpening: Enhance image detail and clarity.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition and resolving issues promptly. This section details routine maintenance and common troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Understanding common malfunctions and their causes helps in proactive maintenance and efficient troubleshooting.
- Low Battery Warnings: Indicates the need for battery charging or replacement.
- GPS Signal Loss: Can be caused by interference or poor satellite visibility. Try relocating to an open area.
- Motor Malfunctions: May be due to damage or debris. Inspect motors and propellers for any damage.
Routine Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance prolongs the lifespan of your drone and ensures optimal performance.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone’s body and propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Battery Care: Store batteries in a cool, dry place and avoid overcharging.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware updated for optimal performance and bug fixes.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems can save time and prevent costly repairs.
- Low Battery Warnings: Charge or replace the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an open area with clear satellite visibility.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors and propellers for damage; replace if necessary.
Troubleshooting Flowchart (Drone Fails to Take Off)
A flowchart provides a structured approach to troubleshooting.
Start: Drone fails to take off -> Check battery level (sufficient? Yes: Proceed to next step, No: Charge/replace battery) -> Check propeller condition (damage? Yes: Replace propellers, No: Proceed to next step) -> Check GPS signal (acquired? Yes: Proceed to next step, No: Relocate to open area) -> Check motor function (all motors spinning? Yes: Check for other issues, No: Inspect/replace motors) -> End
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section Artikels important legal and regulatory considerations.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules in your area before flying.
- Registration: Many jurisdictions require drone registration with the relevant aviation authority.
- Permits: Certain operations, such as commercial flights or flights in restricted airspace, may require permits.
- Airspace Restrictions: Be aware of airspace restrictions, including no-fly zones near airports and other sensitive areas.
Importance of Registration and Permits
Registering your drone and obtaining necessary permits demonstrates responsible operation and helps authorities track drone activity.
Failure to comply can result in fines or legal consequences.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions are implemented to protect public safety and prevent interference with manned aircraft operations.
Examples include areas around airports, military bases, and national parks.
Legally Restricted Scenarios
Several scenarios might legally restrict drone operation.
- Flying over private property without permission.
- Flying near critical infrastructure (power plants, etc.).
- Operating a drone under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Successfully operating a drone involves more than just understanding the controls; it demands a commitment to safety, legal compliance, and continuous learning. From meticulous pre-flight checks to mastering aerial photography techniques, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the exciting world of drone piloting responsibly. Remember, practice makes perfect, and continuous refinement of your skills will lead to increasingly impressive and safe flights.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a good understanding of safety regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including legal considerations and practical techniques, I recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation comes down to thorough preparation and consistent practice.
Quick FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and obstacle avoidance systems.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these aspects, including practical tips and safety procedures, you should consult a resource like this excellent article on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, proficient drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and its implications.
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved locations significantly or experienced any strong magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If GPS signal is lost, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, execute a safe emergency landing procedure.
How do I clean my drone’s propellers?
Gently clean propellers with a soft brush and avoid harsh chemicals. Inspect for damage after cleaning.
What is the best way to store drone batteries?
Store drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Store them at approximately 50% charge when not in use for extended periods.
