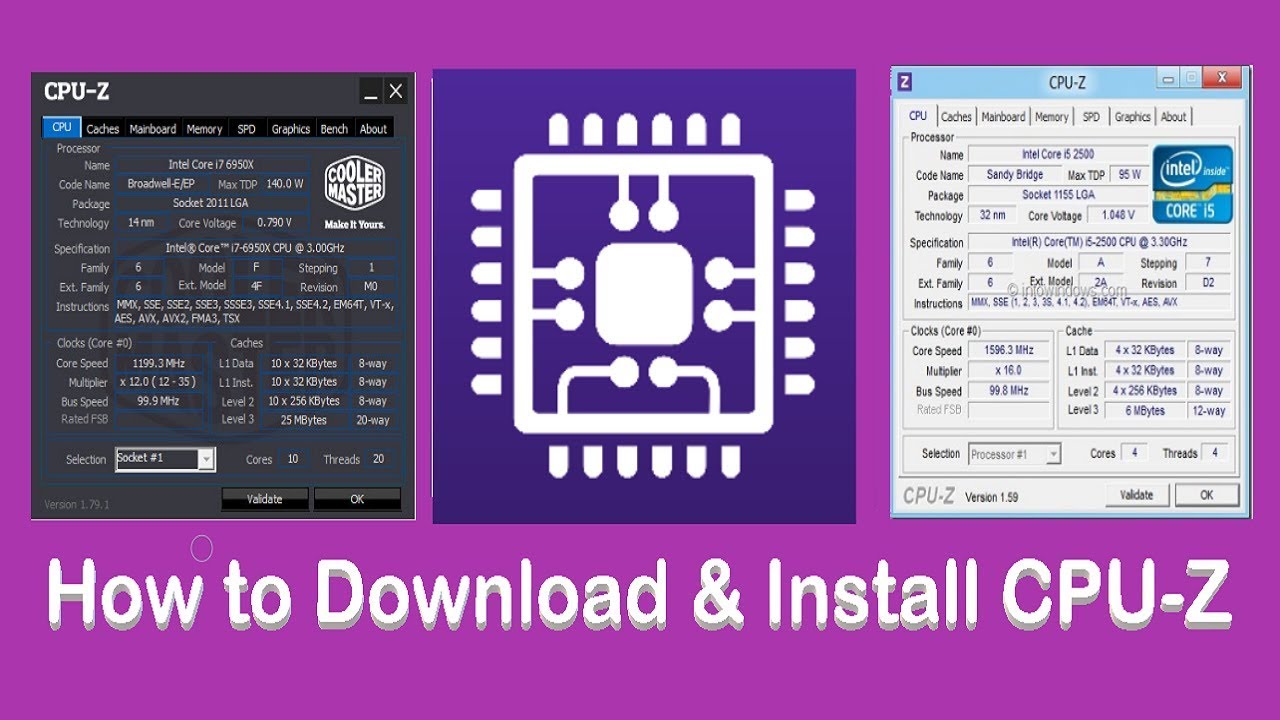
Cpu z – CPU-Z is your go-to tool for easily understanding your computer’s inner workings. This free utility provides detailed information about your CPU, motherboard, RAM, and more, presented in a clear and accessible format. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a curious newcomer, CPU-Z empowers you to quickly identify your system’s components and their specifications.
CPU-Z is great for checking your system specs, right? But to really understand your motherboard’s capabilities, you’ll want to check the detailed specs in the msi b650 gaming plus wifi manual. This will help you get the most out of your CPU, especially when you’re tweaking settings in CPU-Z. Knowing your motherboard’s limitations and features is key to optimizing performance.
From identifying your processor’s model and clock speed to understanding your RAM type and capacity, CPU-Z offers a comprehensive overview. It’s incredibly useful for troubleshooting, comparing hardware, and even verifying compatibility before upgrading components. This guide will walk you through its key features and how to interpret the data it provides.
CPU-Z Functionality Overview
CPU-Z is a freeware utility that provides detailed information about your computer’s hardware components. It’s a valuable tool for identifying CPU specifications, checking system stability, and troubleshooting hardware issues. This section will cover the core functions, data categories, and a step-by-step guide to using CPU-Z.
Core Functions of CPU-Z, Cpu z
CPU-Z’s primary function is to identify and display detailed specifications of various computer components. This includes the CPU, motherboard, RAM, and graphics card. It achieves this through direct access to hardware registers and system information. Beyond identification, it can also be used for basic system monitoring, though it’s not a dedicated monitoring tool.
System Information Categories
CPU-Z organizes system information into several key tabs: CPU, Cache, Mainboard, Memory, SPD, Graphics, and Benchmarks. Each tab provides a comprehensive breakdown of the corresponding component’s specifications and capabilities.
Identifying CPU Specifications with CPU-Z
- Download and install CPU-Z from the official website.
- Run the application. The main window will display various tabs.
- Click the “CPU” tab. This tab provides detailed information about your CPU, including the manufacturer, model, core count, clock speed, and cache sizes.
- Review the information displayed. The “CPU” tab is the most crucial for identifying CPU specifics.
Comparison of System Information Tools
| Feature | CPU-Z | Other Tool 1 (Example: HWMonitor) | Other Tool 2 (Example: Speccy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Identification | Detailed, including stepping | Detailed, but may lack some specific stepping information | Detailed, with visual representation |
| Motherboard Information | Comprehensive chipset and BIOS details | Basic motherboard model | Detailed, including manufacturer and model |
| Memory Information | Detailed, including SPD data | Basic memory size and type | Detailed, including timings and manufacturer |
| Graphics Information | Basic GPU information | Detailed GPU information, including clock speeds and memory | Detailed GPU information, including driver version |
Interpreting CPU-Z Data: Cpu Z
Understanding the data presented by CPU-Z is crucial for effective system analysis. This section provides guidance on interpreting key data points, including clock speeds, cache levels, and motherboard chipset details.
Interpreting CPU Clock Speed Data
CPU-Z displays both the base clock speed and the current clock speed. The base clock speed is the manufacturer’s specified speed, while the current clock speed can vary depending on workload and power management settings. A significant discrepancy between these two values may indicate issues with CPU throttling or overclocking instability.
Significance of CPU Cache Levels
CPU-Z shows the different levels of CPU cache (L1, L2, L3). Each level has a different size and speed, impacting application performance. Larger and faster caches generally lead to better performance, particularly in applications that require frequent data access.
Motherboard Chipset Details
The “Mainboard” tab provides details about the motherboard’s chipset. This information is crucial for determining compatibility with other components and understanding the motherboard’s capabilities. For example, the chipset determines the type and speed of supported RAM and expansion slots.
Interpreting Memory Information
The “Memory” tab provides details about the installed RAM, including the type, size, speed, and timings. Inconsistencies or errors in this section can indicate problems with RAM modules or their configuration. The “SPD” tab provides even more granular details on each individual RAM stick.
CPU-Z and Benchmarking
While CPU-Z doesn’t perform benchmarks itself, its data is valuable for interpreting the results from other benchmarking tools. This section explores the relationship between CPU-Z and benchmarking software.
Comparing CPU-Z and Benchmarking Tool Results
CPU-Z provides the baseline specifications; benchmarking tools measure performance. Comparing the two helps determine if a system’s performance aligns with expectations based on its specifications. For example, a low benchmark score despite high CPU clock speed might indicate other bottlenecks.
Using CPU-Z Data to Interpret Benchmarking Results
CPU-Z data provides context for benchmark results. If a benchmark highlights low memory performance, the “Memory” tab in CPU-Z can help determine if this is due to slow RAM speeds or insufficient capacity.
So you’re checking your CPU specs with CPU-Z, right? That’s great for keeping tabs on your system’s performance. But what if you need to check email while waiting for the ferry? You might want to check out the quality of bc ferries wifi before you start streaming. Once you’re back on solid ground, remember CPU-Z is your friend for troubleshooting any post-voyage tech hiccups.
Limitations of Using CPU-Z Alone for Performance Analysis
CPU-Z primarily identifies hardware; it doesn’t measure performance directly. Using CPU-Z alone for performance analysis is incomplete. It should be used in conjunction with benchmarking tools for a comprehensive evaluation.
Best Practices for Using CPU-Z with Benchmarking Software
- Use CPU-Z to verify system specifications before running benchmarks.
- Compare CPU-Z’s reported specifications to benchmark results to identify performance bottlenecks.
- Use multiple benchmarking tools to obtain a more comprehensive performance assessment.
CPU-Z for Troubleshooting
CPU-Z is a helpful tool for diagnosing CPU-related hardware problems. This section details how CPU-Z assists in identifying and resolving various hardware issues.
Diagnosing CPU-Related Hardware Problems
CPU-Z can help identify problems by comparing the reported specifications to the expected specifications. Discrepancies might point towards issues such as incorrect clock speeds, overheating, or compatibility problems.
Identifying Overheating or Clock Speed Issues
While CPU-Z doesn’t directly measure temperature, unusually high clock speeds (compared to the base clock) might indicate the CPU is trying to compensate for overheating. Cross-referencing with a dedicated temperature monitoring tool is recommended.
Checking for CPU and Motherboard Compatibility
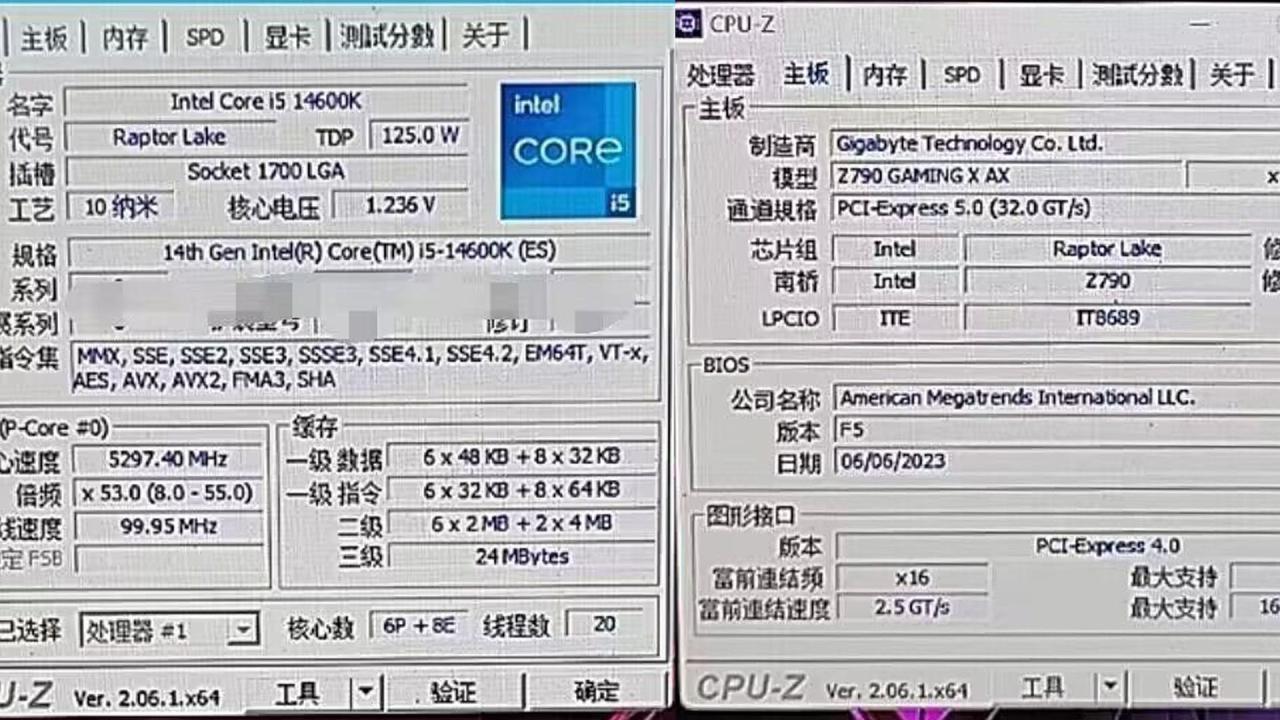
By comparing the CPU socket type reported by CPU-Z with the motherboard’s socket type, compatibility can be verified. Mismatches can lead to system instability or failure to boot.
Troubleshooting Flowchart Using CPU-Z Data
- System Instability: Check CPU clock speeds in CPU-Z. Are they unusually high or low? Check temperatures using a separate monitoring tool. Verify CPU and motherboard compatibility.
- System Failure to Boot: Verify CPU and motherboard compatibility using CPU-Z. Check RAM configuration using CPU-Z’s Memory and SPD tabs.
- Unexpected Performance Issues: Compare CPU-Z’s reported specifications with benchmark results to identify potential bottlenecks.
Advanced CPU-Z Features
Beyond the basic identification features, CPU-Z offers advanced functionality to delve deeper into system specifics. This section covers the advanced tabs and their uses.
Functionality of the “SPD” Tab

The “SPD” tab provides detailed information about each RAM module individually, including timings, voltage, and manufacturer details. This granular information is essential for fine-tuning memory settings and troubleshooting memory-related issues.
Information Provided in the “Graphics” Tab
The “Graphics” tab displays details about the integrated or dedicated graphics card, including the manufacturer, model, and clock speeds. This information is useful for identifying the graphics card and assessing its capabilities.
Identifying Different Processor Types
CPU-Z clearly identifies the processor manufacturer (Intel or AMD) and the specific processor model. This information is crucial for determining compatibility and understanding processor architecture.
Summary of the “Mainboard” Tab Information
The “Mainboard” tab summarizes information about the motherboard, including the manufacturer, model, chipset, and BIOS version. This data is essential for system identification and troubleshooting.
Visual Representation of CPU-Z Data
Visualizing CPU-Z data enhances understanding and facilitates comparisons. This section explores ways to represent key data points visually.
Visual Representation of Key CPU Specifications
A bar chart could effectively display CPU specifications. The x-axis could represent different specifications (clock speed, cache size, core count), and the y-axis would represent the values. Different colored bars could represent different CPUs for comparison.
Hypothetical CPU Architecture Description
Example: A hypothetical Intel Core i7-13700K based on CPU-Z data:
- Architecture: Hybrid architecture with Performance-cores (P-cores) and Efficient-cores (E-cores).
- P-core Count: 8
- E-core Count: 8
- L3 Cache: 30MB
- Base Clock Speed: 3.4 GHz
- Boost Clock Speed: 5.4 GHz
Visual Representation of Memory Information
A pie chart could effectively visualize memory usage. Each segment could represent different types of memory (RAM, VRAM), with the size of each segment proportional to its capacity.
Visual Comparison of Two Different CPUs
A comparative bar chart could effectively display the differences between two CPUs. The x-axis would list the specifications, and the y-axis would show the values for each CPU. Different colors could represent each CPU.
- Compare clock speeds (base and boost).
- Compare core counts and thread counts.
- Compare cache sizes (L1, L2, L3).
- Compare TDP (Thermal Design Power).
Outcome Summary
Understanding your computer’s hardware is crucial for troubleshooting, upgrading, and maximizing performance. CPU-Z provides a straightforward way to access this vital information. By mastering its features, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of your system and be better equipped to handle any hardware-related challenges. So, download CPU-Z, explore its capabilities, and unlock the secrets of your PC!
Quick FAQs
Is CPU-Z safe to use?
Yes, CPU-Z is a safe and reputable tool. It’s a lightweight utility that doesn’t install any unwanted software.
Can CPU-Z damage my computer?
No, CPU-Z is purely informational; it doesn’t modify any system settings or hardware.
So you’re checking your CPU specs with CPU-Z, right? It’s a handy tool for that. But did you know that understanding your system’s capabilities is just as important as knowing the rules of the airspace, especially if you’re thinking about flying a drone? Check out the specifics on canada drone laws under 250g before you take to the skies.
Back to CPU-Z, remember to monitor your CPU temperature while running those demanding drone simulations!
Where can I download CPU-Z?
Download CPU-Z from the official CPUID website to ensure you get the latest version and avoid potentially harmful downloads.
How often should I use CPU-Z?
Whenever you need to check your system specifications, troubleshoot problems, or before making hardware upgrades.